8 Email Deliverability Best Practices to Master in 2025
- Prince Yadav
- Jun 23, 2025
- 14 min read
Why Your Emails Aren't Landing in the Inbox (And How to Fix It)
In B2B marketing, hitting 'send' is just the first step. The real challenge is ensuring your message actually reaches the primary inbox, not the dreaded spam folder. This is where mastering email deliverability becomes non-negotiable for any business serious about scalable growth, from SaaS startups to established e-commerce brands. Poor deliverability doesn't just waste effort; it actively damages your sender reputation, sabotages your lead acquisition funnel, and hurts your bottom line. With mailbox providers like Google and Yahoo enforcing stricter sender requirements, understanding both the technical and strategic nuances is more critical than ever.
This guide moves beyond generic advice to provide a comprehensive roundup of the most essential email deliverability best practices. We will dissect each critical component, from foundational domain authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) and list hygiene to advanced strategies like IP warm-ups and feedback loop management. You will gain actionable steps, practical examples, and expert insights to build a robust sending infrastructure. Following these practices will help you cultivate a pristine sender reputation and ensure your carefully crafted messages consistently connect with your target audience, driving appointments and revenue.
1. Authenticate Your Email Domain (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
Authenticating your email domain is a foundational step in any serious email outreach strategy. It's the process of proving to inbox providers like Google and Microsoft that you are who you say you are. This technical setup involves three key protocols: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. Together, they act as your domain's digital passport, verifying legitimacy and protecting your brand's reputation from spoofing and phishing attacks. Implementing these is a critical factor in achieving strong email deliverability best practices.
How Email Authentication Works
Authentication isn't just one action but a layered defense system you build within your domain's DNS settings.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework): This is the first layer. You create an SPF record, which is a simple text file listing all the specific IP addresses and servers authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain. When an email is received, the recipient’s server checks if the sending server is on your approved list.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): This adds a tamper-proof digital signature to your emails. The signature is created using a private key, and the recipient server uses a public key (published in your DNS) to verify it. A valid DKIM signature proves that the email content hasn't been altered in transit.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance): DMARC unites SPF and DKIM. It tells receiving servers what to do if an email fails either SPF or DKIM checks, instructing them to either monitor (), quarantine (), or reject () the message. It also provides valuable reports on who is sending email from your domain.
The following infographic illustrates the recommended implementation flow for these authentication protocols.
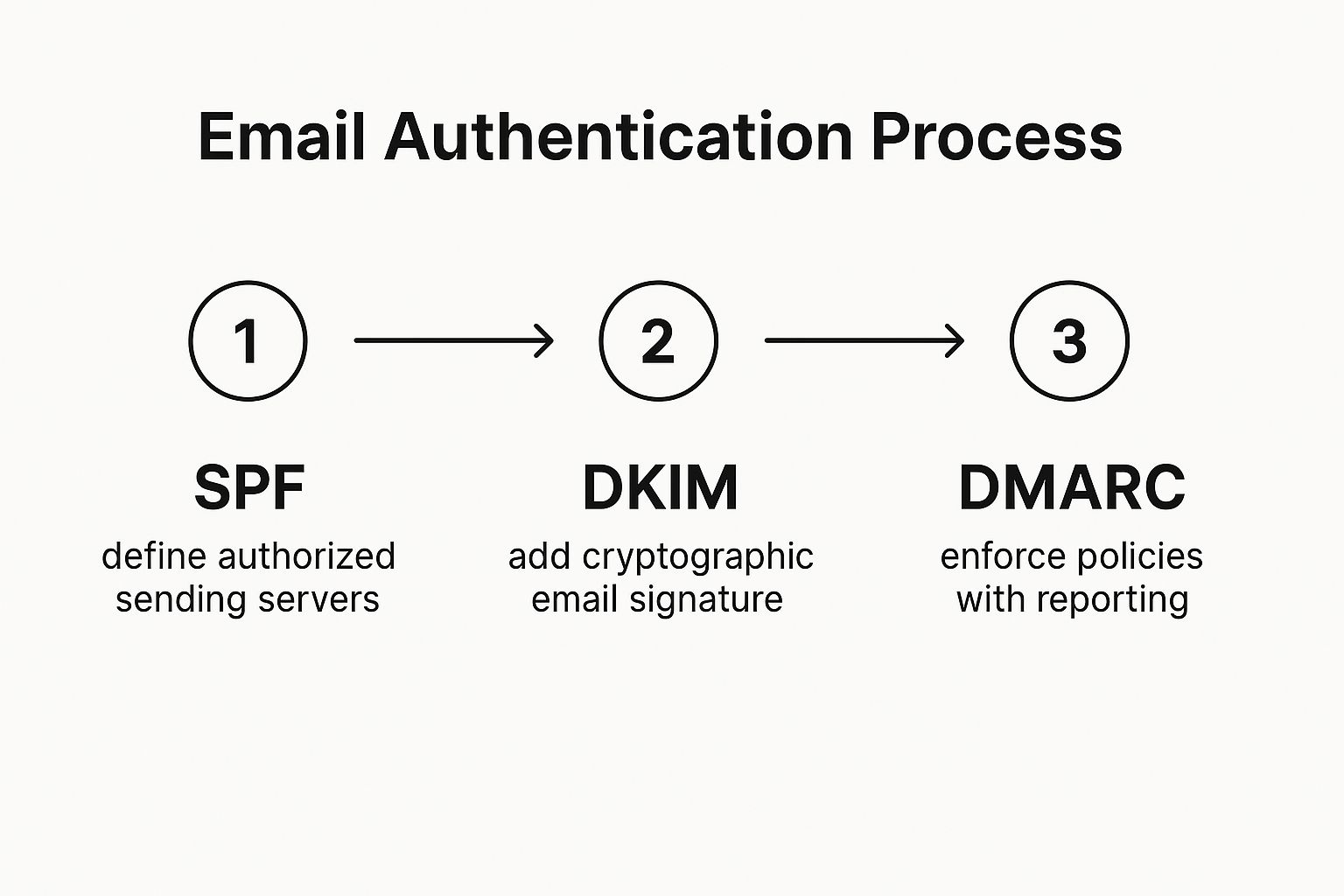
This step-by-step process ensures a stable and monitored rollout, preventing accidental disruption of your legitimate email streams while building a robust defense. For a deeper technical dive, you can learn more about how to improve email deliverability for your agency.
2. Maintain List Hygiene and Segmentation
Sending emails to a clean, engaged list is just as crucial as authenticating your domain. List hygiene is the ongoing process of removing invalid, inactive, and unengaged subscribers from your lists. Segmentation involves organizing the remaining subscribers into smaller, targeted groups based on their behavior, demographics, or preferences. This dual approach ensures your messages are relevant and welcomed, directly boosting engagement metrics and protecting your sender reputation. A pristine, well-organized list is a cornerstone of high-performing email deliverability best practices.

How List Hygiene and Segmentation Work
Think of your email list as a garden. Without regular weeding and organization, it becomes overgrown and unproductive. A healthy list yields better results by focusing your efforts on recipients who are genuinely interested.
List Hygiene: This is the "weeding" process. It involves proactively identifying and removing problematic email addresses. Hard bounces (permanent failures) should be removed immediately. Soft bounces (temporary failures) should be monitored and removed after a few unsuccessful attempts. Regularly using verification services to scrub your list for invalid or risky addresses, like "accept-all" mailboxes, is also essential.
Segmentation: This is the "organizing" part. Instead of sending the same message to everyone, you divide your audience into meaningful segments. For example, Amazon micro-segments based on browsing and purchase history, while HubSpot uses engagement scoring to automatically group users by how often they open emails or click links. This allows for highly personalized and relevant content that drives better engagement.
Sunset Policies: This combines both practices. A sunset policy is an automated rule that removes subscribers who have been consistently unengaged for a specific period (e.g., 90-180 days). This keeps your list fresh and focused on your most active audience members.
Implementing these practices reduces bounce rates, spam complaints, and unsubscribe requests, which are all positive signals to inbox providers. To ensure your list is as clean as possible, you can learn how to validate accept-all emails and other risky contacts.
3. Optimize Send Frequency and Timing
Beyond the technical setup, the human element of your sending schedule is paramount. Optimizing your send frequency and timing involves a strategic approach to when and how often you contact subscribers. It's about finding the delicate balance between maintaining a presence in the inbox and causing email fatigue, which can lead to unsubscribes, or worse, spam complaints. A well-timed, well-paced sending cadence signals to inbox providers that you respect recipient preferences, a key component of modern email deliverability best practices.
How Frequency and Timing Impact Deliverability
Inbox providers like Google and Microsoft closely monitor how recipients interact with your emails. Sending too frequently to an unengaged segment can quickly lower your open rates and increase complaint rates, damaging your sender reputation. Conversely, sending too infrequently can cause subscribers to forget who you are, also leading to spam reports. The goal is to align your sending schedule with audience expectations and engagement patterns, proving you send valuable, timely content.
Frequency: This is about how often you send. A daily email might work for a news outlet like The New York Times, but it could be overwhelming for an e-commerce brand. The key is to match frequency to the value you provide and the subscriber's lifecycle stage.
Timing: This refers to the specific day and time you send. While industry benchmarks provide a starting point, true optimization comes from analyzing your own data. For example, a B2B SaaS company might find success sending mid-week during business hours, while a B2C entertainment brand like Netflix sends personalized recommendations on Friday evenings when users are planning their weekend viewing.
Personalization: The most advanced strategies allow subscribers to set their own preferences. Giving users a choice between daily, weekly, or monthly digests empowers them and provides you with invaluable data, directly improving engagement and deliverability.
By systematically testing and adjusting your schedule, you demonstrate to inbox providers that you're a responsible sender focused on user experience. This approach helps you maintain high engagement metrics, which are critical for long-term inbox placement. For a more detailed analysis on this topic, you can learn more about the best time to send cold emails in 2025.
4. Create Relevant and Engaging Content
While technical setups are crucial, the content of your emails is what ultimately determines how subscribers interact with your messages, directly influencing your sender reputation. Creating relevant and engaging content means moving beyond generic blasts to deliver value that resonates with your audience's specific needs and interests. This focus on quality encourages positive engagement signals like opens, clicks, and replies, which inbox providers use as a key indicator of a legitimate, wanted sender. Mastering this is one of the most impactful email deliverability best practices.

How Engaging Content Improves Deliverability
Inbox providers monitor how recipients interact with your emails to judge their quality. High engagement signals that your emails are valued, while low engagement (or high complaints) signals that they are unwanted spam.
Positive Signals: When users open, click, forward, or reply to your emails, it tells providers like Google and Microsoft that you are a trusted sender. For example, Grammarly sends personalized weekly writing reports that users actively look forward to, generating consistent positive engagement.
Personalization and Value: Generic content gets ignored. Use segmentation and dynamic content to tailor messages. Sephora excels here, sending product recommendations based on a user's purchase history and previously identified beauty preferences, making each email feel like a personal consultation.
Negative Signals: High unsubscribe rates, spam complaints, and low open rates are red flags. These negative signals damage your sender reputation and can cause your emails to be filtered directly to the spam folder. A clear unsubscribe link, while seemingly counterintuitive, actually helps by preventing frustrated users from marking you as spam.
By consistently providing content that your audience wants to receive, you build a positive sending history that inbox providers reward with better inbox placement.
5. Monitor Sender Reputation and Metrics
Proactive monitoring is just as crucial as the initial setup of your email infrastructure. Once you start sending, you must continuously track your sender reputation and key performance metrics. This ongoing analysis allows you to catch deliverability issues before they escalate and damage your campaign performance. Tools from major inbox providers and third-party services give you a direct view into how your domain is perceived, forming an essential feedback loop for maintaining strong email deliverability best practices.
How Sender Reputation Monitoring Works
Sender reputation is a score that inbox providers assign to your sending domain and IP address. A higher score means your emails are more likely to land in the inbox, while a low score can lead to the spam folder or outright rejection. Monitoring involves tracking this score alongside other critical data points.
Sender Reputation Scores: Services like Validity's Sender Score or Barracuda's reputation lookup provide a numerical score (typically 0-100) that summarizes your sending health. This is a quick, high-level indicator of how trustworthy you appear to mailbox providers.
Inbox Provider Tools: Major providers offer their own feedback systems. Google Postmaster Tools provides specific data on your reputation within the Gmail ecosystem, including spam complaint rates, domain reputation, and authentication success. Microsoft's Smart Network Data Services (SNDS) offers similar visibility for Outlook.com.
Engagement & Performance Metrics: Beyond reputation scores, you must track metrics like bounce rates, spam complaint rates, and engagement (opens, clicks). A sudden spike in hard bounces or complaints is a red flag that requires immediate investigation. These metrics are the leading indicators of potential reputation damage.
Setting up these monitoring systems gives you the data needed to make informed decisions. You can identify problematic campaigns or list segments and take corrective action before your sender reputation suffers long-term harm. For a more comprehensive look at what to track, you can explore the top email marketing KPIs that actually drive business growth.
6. Implement Double Opt-In Processes
Implementing a double opt-in process is a powerful strategy for building a high-quality, engaged email list from the very beginning. Unlike single opt-in, where a user is added immediately after submitting their email, double opt-in adds a crucial verification step. The new subscriber must click a confirmation link sent to their inbox, proving the email address is valid and that they genuinely want to receive your communications. This method builds a foundation of consent and engagement, which is a core tenet of modern email deliverability best practices.
How Double Opt-In Strengthens Deliverability
The double opt-in process acts as a quality filter for your email list, directly impacting how inbox providers perceive your sending reputation. It prevents spam traps, typos, and low-interest contacts from ever making it onto your active list.
Verifies Email Validity: This process confirms that the email address is not only real but also actively monitored by the subscriber. This significantly reduces your bounce rate, a key metric that inbox providers use to judge sender reputation.
Confirms Subscriber Intent: By taking the extra step to confirm, subscribers signal a higher level of interest. This leads to better open rates, click-through rates, and fewer spam complaints down the line. Engaged recipients are the best signal you can send to ISPs like Google and Microsoft.
Ensures Compliance: In regions with strict data privacy laws like the GDPR in Europe, double opt-in provides clear, auditable proof of consent. Companies like AWeber have long championed this approach, and it’s a standard for businesses operating under or marketing to European customers.
By prioritizing quality over quantity, double opt-in ensures your emails reach people who actually want them. This creates a positive feedback loop that boosts your sender score and keeps your messages out of the spam folder.
7. Manage Complaint Rates and Feedback Loops
Actively managing spam complaints is a non-negotiable part of maintaining a healthy sender reputation. When a recipient marks your email as spam, it sends a powerful negative signal to their inbox provider. Systematically monitoring these complaints through ISP feedback loops allows you to understand what isn't working and take corrective action immediately. This proactive management is a cornerstone of modern email deliverability best practices, protecting your domain from being blacklisted and ensuring your messages reach their intended audience.
How Complaint Management and Feedback Loops Work
Feedback Loops (FBLs) are a direct line of communication from major Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to you. When a subscriber complains, the FBL sends an automated report back to the sender. This allows you to remove the complaining address from your list instantly, which is critical for keeping complaint rates low.
Setting Up FBLs: You must register with each major ISP's program to receive these reports. Key programs include the Gmail Feedback Loop, Yahoo Complaint Feedback Loop, and Microsoft’s Junk Mail Reporting Program (JMRP). Most high-quality Email Service Providers (ESPs) handle this process for you automatically.
Monitoring Complaint Rates: Your goal is to keep your complaint rate consistently below 0.1% (1 complaint per 1,000 emails sent). Rates higher than this will trigger ISP filters and severely damage your deliverability.
Analyzing and Acting on Data: Use complaint data to diagnose problems. A sudden spike after a new campaign could indicate issues with the subject line, content, or audience targeting. Consistently high complaints from a specific list segment suggest a problem with the lead source or a mismatch in expectations.
Suppressing complainers is the first step, but the real value comes from using the data to refine your strategy. For example, if you see high complaints on outreach to a specific industry, you might need to adjust your messaging or value proposition. You can discover more about refining your outreach by exploring these cold email tips to book more meetings.
8. Warm Up IP Addresses and Domains Gradually
Warming up your sending infrastructure is the systematic process of building a positive reputation for a new IP address or domain. You cannot simply start sending thousands of emails from a new source and expect success. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) view sudden, high-volume activity from an unknown sender as highly suspicious. A gradual warm-up process builds trust with mailbox providers like Gmail and Outlook, demonstrating that you are a legitimate sender and not a spammer. This methodical approach is a cornerstone of long-term email deliverability best practices.
How the Warm-Up Process Works
The core principle of a warm-up is to start small and incrementally increase your sending volume over a set period. This allows ISPs to observe your sending patterns, monitor recipient engagement, and gradually build confidence in your mail stream. Rushing this process is one of the fastest ways to damage your sender reputation permanently.
Start with Engaged Segments: Begin by sending to your most active and engaged subscribers. These are users who are likely to open and click your emails, sending strong positive signals to ISPs that your content is wanted.
Gradual Volume Increase: A common schedule involves starting with 50-100 emails on day one and doubling the volume every few days, provided your metrics remain healthy. This slow ramp-up appears natural and non-threatening to ISP filtering algorithms.
Monitor Key Metrics: Throughout the process, you must meticulously track your open rates, click rates, bounce rates, and spam complaint rates. Any negative spikes, such as high bounces or complaints, are a sign to pause the volume increase and diagnose the issue.
This strategy is essential for any business launching a new email program, migrating to a new Email Service Provider (ESP), or dedicating a new IP address for a specific purpose, such as transactional emails versus promotional campaigns. For example, an e-commerce brand preparing for the holiday season might warm up a new IP in October to ensure it's ready for the high volume of Black Friday. Properly executing this ramp-up ensures your messages land in the inbox when it matters most.
Email Deliverability Best Practices Comparison
Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Authenticate Your Email Domain (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) | High – requires technical setup and ongoing maintenance | Moderate – DNS configuration and monitoring tools needed | Strong email legitimacy, reduced spoofing, better inbox placement | Organizations sending bulk emails, brands needing anti-phishing protection | Protects brand, required by major providers, detailed failure reports |
Maintain List Hygiene and Segmentation | Medium – ongoing list cleaning and segmentation logic | Moderate – data management and segmentation tools | Improved engagement, fewer bounces, sender reputation maintained | Brands with large or aging email lists aiming for higher relevance | Higher open/conversion rates, reduced spam complaints, cost savings |
Optimize Send Frequency and Timing | Medium to High – requires data collection and testing | Moderate to High – marketing automation and analytics | Increased open rates, lower unsubscribe rates, better engagement | Senders needing to balance frequency and avoid fatigue | Maximizes campaign effectiveness, improves subscriber retention |
Create Relevant and Engaging Content | Medium to High – needs creative and data resources | High – content creation, personalization, design | Significantly higher engagement and conversions | Brands aiming to build strong subscriber relationships | Builds trust, improves reputation, drives conversions |
Monitor Sender Reputation and Metrics | Medium – requires setup of monitoring tools and analysis | Moderate – monitoring platforms and expertise needed | Early detection of deliverability issues, data-driven decisions | Professional email marketers focused on maintaining sender score | Prevents reputation damage, improves ROI, actionable insights |
Implement Double Opt-In Processes | Low to Medium – setup confirmation workflow | Low to Moderate – email platform support required | Higher list quality, reduced bounces, confirmed subscriber intent | Regulatory compliance needs, B2B lists, quality-focused marketers | Reduces invalid addresses, legal protection, improves engagement |
Manage Complaint Rates and Feedback Loops | Medium – ISP integrations and complaint monitoring | Moderate – technical setup and ongoing maintenance | Maintained reputation, fewer spam complaints | Large senders with complaint management needs | Direct ISP feedback, prevents reputation damage, improves email program |
Warm Up IP Addresses and Domains Gradually | Medium to High – planned gradual volume increases | Moderate – time and monitoring required | Positive sender reputation, reduced risk of blacklisting | New IP/domain senders, scaling email volume senders | Builds long-term reputation, prevents deliverability issues, trust with ISPs |
Turning Deliverability Insights into Business Growth
Navigating the complexities of email outreach can feel like a high-stakes game, but mastering the rules of deliverability shifts the odds decisively in your favor. This comprehensive guide has detailed the critical pillars for success, moving beyond surface-level tips to provide a strategic blueprint. By now, it should be clear that achieving consistent inbox placement is not about finding a single secret trick; it is the result of a deliberate, multi-faceted strategy.
The journey begins with a non-negotiable technical foundation. Properly configuring SPF, DKIM, and DMARC is your passport into the world of legitimate email, telling mailbox providers that your messages are authentic and trustworthy. From there, the focus shifts to the quality of your audience. Diligent list hygiene, strategic segmentation, and respectful double opt-in processes ensure you are communicating with an engaged audience that wants to hear from you, drastically reducing the risk of spam complaints and bounces.
From Technical Setup to Strategic Execution
Once your foundation is solid, your ongoing actions determine your long-term success. The principles we’ve covered are not "set it and forget it" tasks; they are continuous disciplines.
Strategic Cadence: Implementing a thoughtful warm-up process for new domains and IPs, combined with optimizing your send frequency, builds and sustains a positive sender reputation. Rushing this step is one of the most common and damaging mistakes a B2B business can make.
Proactive Monitoring: Success in email deliverability requires vigilance. Consistently monitoring your sender reputation, tracking key metrics like open and bounce rates, and actively managing complaint feedback loops allow you to identify and resolve issues before they escalate and cause significant damage to your domain’s health.
Content as a Deliverability Tool: Ultimately, the content of your emails is a powerful deliverability factor. Crafting relevant, engaging, and personalized messages that resonate with your audience leads to higher open rates, more replies, and fewer spam reports. These positive engagement signals are precisely what ISPs look for when deciding where to place your emails.
The True Value of Mastering Email Deliverability
Embracing these email deliverability best practices transforms your outreach from a speculative cost center into a predictable, scalable revenue driver. Each element, from domain authentication to content personalization, works in concert to build a powerful system. This system not only ensures your messages land in the primary inbox but also fosters trust and strengthens relationships with your prospects and customers. For B2B organizations, especially those in SaaS, tech, and e-commerce, this translates directly into more booked meetings, a healthier sales pipeline, and sustainable business growth. The effort invested in deliverability pays dividends by making every other aspect of your email marketing more effective.
Tired of wrestling with technical setups and constantly worrying about your sender reputation? Fypion Marketing specializes in managing the entire deliverability lifecycle, from domain warm-up to campaign execution, so you can focus on what you do best: closing deals. Partner with us to turn these best practices into a reliable stream of qualified, pay-per-meeting appointments. Learn how Fypion Marketing can build your predictable sales pipeline.
Comments